
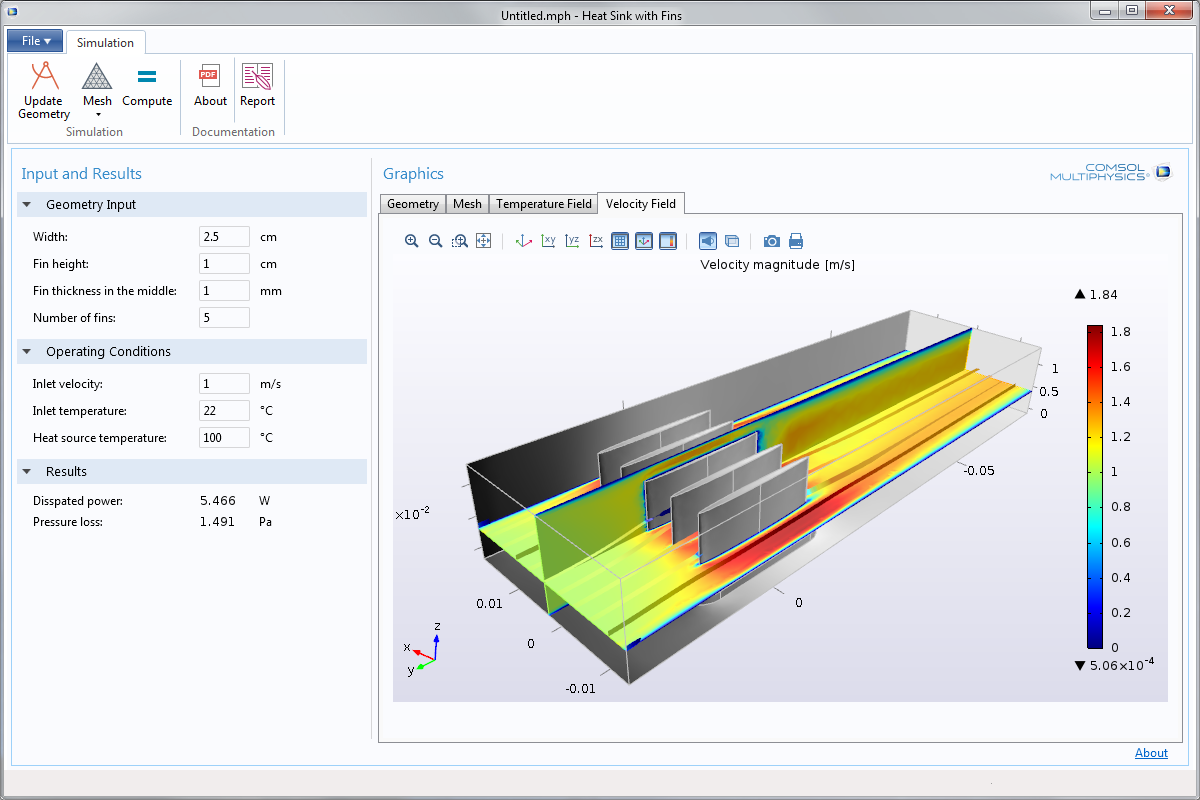
It also provides a quick introduction to creating applications using the Application Builder. Two-dimensional numerical modelling of the stationary flow around a blade of the Achard turbine, a new water-current turbine concept, is performed both with COMSOL Multiphysics 3.3 and with Fluent 6. View screenshot > Terminal feature improved.
#How to take integral a surface in comsol 5.1 how to
It provides an overview of the COMSOL ® environment with examples that show you how to use the COMSOL Desktop ® user interface and the Model Builder. However, I cannot figure out how to use the system with my results, as they still seem to be in cartesian form. Read this book if you are new to COMSOL Multiphysics®. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential. The process of finding integrals is called integration. I have decided to use the cylindrical coordinate system, and have added it under my definitions. In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data.

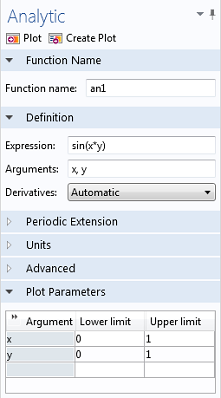
I've been using cartesian coordinates, which I believe my gives me the correct force in the z axis (the direction of flow), but however does not given an useful representation in the x and y axis. As no transverse approximation is imposed, it remains accurate even for so-called quasi-TM and -TE modes of low, finite azimuthal mode order, as are relevant to applications in non-linear/quantum optics. I'm in the process of trying to find the pressures exerted by a flow onto a turbine using the pressure. The method exploits COMSOLs ability to accept the definition of solutions to Maxwells equations in so-called weak form.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
